Cyber threat from abroad on the rise
 0 Comment(s)
0 Comment(s) Print
Print E-mail China Daily, March 20, 2012
E-mail China Daily, March 20, 2012
Cyber attacks on China launched from bases overseas surged in 2011, rising to 8.9 million computers affected from 5 million the previous year, according to a network security report.
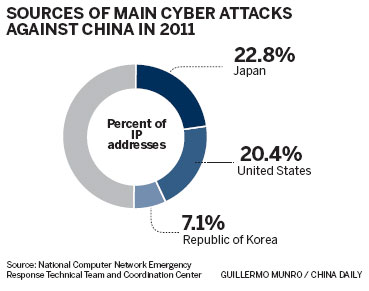
Japan was the source of most attacks (22.8 percent), followed closely by the United States (20.4 percent) and the Republic of Korea (7.1 percent).
The report, released on Monday by China's National Computer Network Emergency Response Technical Team and Coordination Center, found that 11,851 Internet protocol addresses based overseas had controlled 10,593 Chinese websites last year.
"This shows that Chinese websites still face a serious problem from being maliciously attacked by foreign hackers or IP addresses," Wang Minghua, deputy director of the team's operation department, said at a news conference on Monday.
Attacks included destroying servers, distorting website content and stealing personal data from Chinese Web users.
Overseas hackers altered the content of 1,116 Chinese websites, including 404 run by government agencies, Wang told China Daily, adding that they may have been responsible for many more, as the addresses and names they use are often difficult to trace.
Although it was discovered that many hackers used Trojan Horse-style programs simply to steal personal data, Zhou Yonglin, director of the team's operation department, said "money is not the sole motivation", as in several cases the hackers had intended to access State networks and steal confidential information.





