Remarkable Achievements in 60 Years: Underpinnings of Rapid Economic Growth
(II) Clean and Efficient Utilization of Coal In addition to optimization of primary energy structure, Chinese government is also dedicated to clean and efficient utilization of coal by increasing coal processing and reducing its percentage in terminal consumption.
In 1980, the terminal consumption of coal accounted for 63.6%, compared with 25.2% in 2007. Coal consumption for power generation accounted for merely 9.7% in 1953, rising to 20.1% in 1978 and 50.5% in 2007.
2. Coal Consumption for Power Generation as a Percentage of Total Coal Consumption
With the overall national strength rising and the technologies growing, coal-fired power generation units have been upgraded continuously in China. By the end of 2008, eleven 1 millionKW super-critical units had been put into service, the 600,000KW and higher thermal power units accounted for 31.27% on a comparable basis, 300,000KW and higher thermal power units accounted for 65.18%, and the percentage of less-than-100,000KW thermal power units declined to 13.38%.
 |
|
1000MW Super-critical Thermal Power Unit of Huaneng Yuhuan Power Plant |
In addition to accelerated construction of clean and efficient units, energy-intensive and heavy-polluting small thermal power units are eliminated as a faster pace. As of 30 June 2008, 7,467 small thermal power units were removed during the 11th Five-year Plan, totaling 54.07 million kW and saving about 160 million tons of crude coal. 1.06 million tons of SO2 emission and 124 million tons of CO2 emission can be eliminated a year.
 |
|
Elimination of Small Thermal Power Units |
Efforts are gradually intensified in energy conservation and environmental protection. All new thermal power plants are equipped with desulfurization units, and existing power plants are upgraded for desulfurization. By the end of 2008, 363 million kW desulfurized thermal power units were put into operation, accounting for 60.4% of the national total of thermal power capacity. Denitrification facilities are provided in some large thermal power plants.
Upgrading of generating units has resulted in rapid decline in coal consumption and continuous rise in power generation efficiency. In 2008, the standard coal consumption of 6,000 kW and higher power plants was 322 g/kW.h nationwide, down 91 g from 1980; the station service power consumption rate was 5.9%, down 0.5 percentage point from 1980; the circuit loss rate was 6.8%, down 2.1 percentage points from 1980.
 |
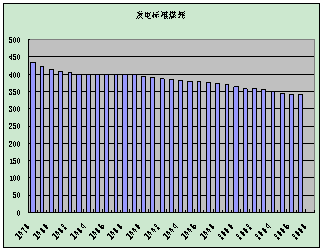 |
| Circuit Loss Rate (Unit: %) | d Coal Consumption for Power Generation (Unit: g/kW.h) |
 0
0 






